Upper Midwest Environmental Sciences Center
Graphical Vegetation Database Browser Help Page
Help Topics
|
Help Using the Graphical Vegetation Database Browser About the Graphical Vegetation Database BrowserThe graphing software used for the Graphical Vegetation Database Browser was written using Java Applet technologies. To work on your computer, your Web browser must have java enabled. The graphing software displays data for the Long Term Resource Monitoring Program field stations at the same time. The user then can choose one of the graphs to be displayed in more detail in the main window. The software also allows for printing and for creating a comma-delimited text document of the data that can be saved to the user's computer. Using the Graphical Vegetation Database Browser
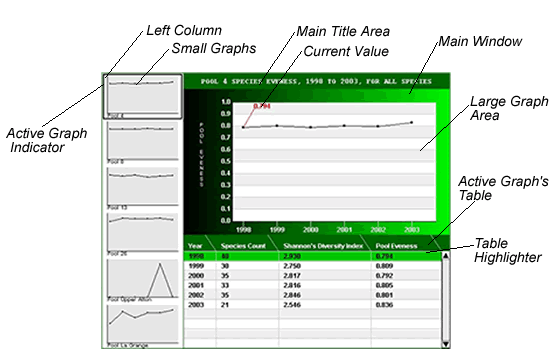
Above is a display of output from the graphing tool. The display is divided into two regions, the left column and the main window. In the left column, small graphs (one for each field station) are displayed. The main window displays the active graph and its associated data table. To change the active graph, point the mouse arrow at the smaller version of the graph in the left column. This highlights the chosen graph, displaying it in the main window. To see a numerical value on the graph in the main window, use the mouse to point to the location on the graph that you want to see the value for or point to a specific year or value in the table. To print a graph, use the dialog box below the main window (shown here):
Select which graphs you wish to print by clicking on pools in the drop-down box, if you hold the control key while selecting pools, multiple selections can be made. Now click on the "Create Charts" button. The selected graphs displays in a new window. Within this new window, click the print icon of your browser and the graphs will be printed, one per page. You may be able to print from the main window, but results are unpredictable depending on the browser and printer used. Another feature provided on the main window is the ability to create a comma-delimited text document by clicking the link below the printing information. This opens a new window containing a text document with header information followed by the data for all six field stations. You will have to save this page by clicking the "File" menu followed by "Save as." Give the file a name and location to be saved then change the file type from .html to .txt and click "Save." You can import the comma-delimited text file into other applications for custom graphing or statistical analysis. Enabling Java in Internet Explorer and Netscape Navigator Internet Explorer
Netscape Navigator
|
StrataThe LTRMP stratifies vegetation sampling by depth as well as across six strata, characterized
by enduring geomorphic and physical features. All sampling points are located in water less than 2.6 m deep. Several strata are further divided within Pool 4 (main channel border, side channel, contiguous backwater, and Lake Pepin) and Pool 26 (main channel border, backwater isolated). Pool 4 is divided by a line through Lake Pepin at river mile 775 into upper and lower sections. These two sections display distinctly different vegetation dynamics. The lower 12 miles of the Illinois River is sampled along with Pool 26. This area is analyzed separately from the rest of Pool 26. The LTRMP vegetation sampling strata are defined as follows: Main Channel BorderAquatic areas between the margins of the main navigation channel and the nearest shoreline (island or mainland) excluding dams, lock walls, and wing dams. Side ChannelThis stratum is characterized by secondary and tertiary channels that have terrestrial margins and measurable current velocities at normal water elevations.Backwater ContiguousBackwater contiguous is characterized by having some connection by water to the main navigation channel but is separated from the main channel by a terrestrial area and does not carry flow at normal river elevations. Backwaters may consist of floodplain depression lakes, sloughs, lateral levee lakes, bays, and artificial lacustrine areas. Backwater IsolatedBackwater isolated is characterized by having no connection by water to the main navigation channel, but may be connected during floods. ImpoundedImpounded areas are large, mostly open-water areas located immediately upriver from locks and dams. Water elevations are held above preimpoundment levels by the dams. Impounded areas may contain submerged channels and areas that were terrestrial before impoundment. Lake PepinLake Pepin is a large natural lake in Pool 4 that was created by the Chippewa River delta. All StrataWithin the Graphical Vegetation Database Browser, strata listed above represent a spatially defined area of a study reach that is smaller than the study reach itself. Estimates from each of the stratum listed above are "pooled" and appropriate "weighting factors" are applied to derive an unbiased estimate for the entire study reach from the collection of strata-specific estimates. Thus, the ALL strata represents an unbiased estimate at the study reach scale, which is larger in physical size than the stratum. return to top |
Life FormsSubmergent SpeciesAll parts of the plant are below the surface of the water. Some plants extend the flower or fruit above the surface. Some pondweeds have submersed and floating leaves but are included in the submergent life form. Rooted Floating-leaf SpeciesThe roots and stems are buried in the sediment. Leaves and flowers float on the surface of the water or occasionally rise above the surface. Emergent SpeciesThe roots are buried in the sediment whereas the stem, leaves, and flowers rise out of the water. Filamentous algaeA nonvascular plant that looks like strands of green hair. It often covers other aquatic plants. return to top |